Abstract
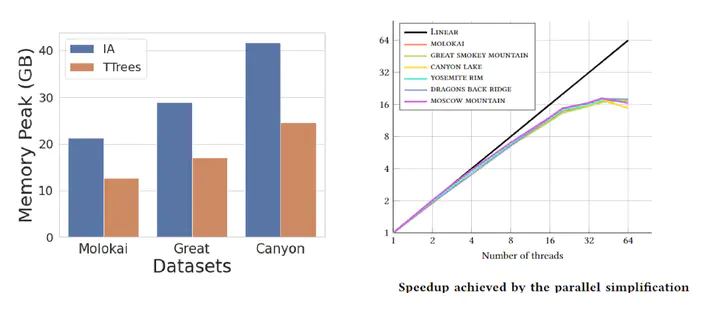
A common first step in the terrain processing pipeline of large Triangulated Irregular Networks (TINs) is simplifying the TIN to make it manageable for further processing. The major problem with TIN simplification algorithms is that they create or remove critical points in an uncontrolled way. Topology-aware operators have been defined to solve this issue by coarsening a TIN without affecting the topology of its underlying terrain, i.e., without modifying critical simplices describing pits, saddles, peaks, and their connectivity. While effective, existing algorithms are sequential in nature and are not scalable enough to perform well with large terrains on multicore systems. Here, we consider the problem of topology-aware simplification of very large meshes. We define a topology-aware simplification algorithm on a compact and distributed data structure for triangle meshes, namely the Terrain trees. Terrain trees reduce both the memory and time requirements of the simplification procedure by adopting a batched processing strategy of the mesh elements. Furthermore, we define a new parallel topology-aware simplification algorithm that takes advantage of the spatial domain decomposition at the basis of Terrain trees. Scalability and efficiency are experimentally demonstrated on real-world TINs originated from topographic and bathymetric LiDAR data. Our experiments show that topology-aware simplification on Terrain trees uses 40% less memory and half the time than the same approach implemented on the most compact and efficient connectivity-based data structure for TINs. Beyond that, our parallel algorithm on the Terrain trees reaches a 12x speedup when using 20 threads.